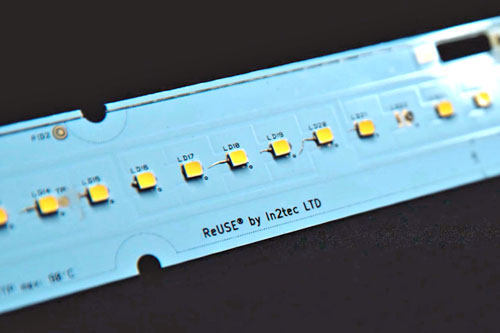
In2tec, a UK-based sustainable electronics specialist, has introduced a technology designed to make industrial LED boards more circular, repairable, and resource-efficient.
The company’s ReUSE and ReCYCLE processes allow the boards to be fully disassembled and reused, significantly reducing carbon emissions and electronic waste.
In2tec’s approach enables the materials and components to be recovered and reused at end-of-life.
‘We’re seeing a 62.5 per cent reduction in carbon dioxide emissions during manufacture compared to conventional printed circuit board assemblies,” Emma Armstrong, sustainable electronics ambassador at In2tec, told the Circular Lighting Report.
‘And with over 20 million LED boards sold annually, that translates to nearly 3.9 million kilograms of carbon dioxide saved – every year.’
At the core of this approach is ReUSE, a design method that allows printed circuit boards to be separated at end-of-life without damaging components.
Combined with ReCYCLE, a low-energy recovery process, it enables manufacturers to reclaim materials such as substrates and electronic parts for reuse in future production.
This method aims to address one of the biggest sustainability challenges in industrial lighting: the premature disposal of components that could otherwise be repaired or repurposed.
In2tec’s approach integrates sustainability at the design stage, ensuring that each assembly can be repaired or broken down for material recove.
‘We’re not just reducing emissions,’ says Armstrong. ‘We’re changing how electronics are made and unmade.
‘This is about designing lighting systems that work for the planet, not just the bottom line.’
ReUSE technology is compatible with both traditional and alternative substrates, including FR4, PET, and aluminium.
According to In2tec, it achieves bond strengths close to solder while operating at significantly lower temperatures, reducing energy use during manufacture and recycling.
For manufacturers, potential benefits include:
• Reduced production emissions
• Lower energy consumption during manufacture
• Improved repairability and reuse
• Greater material recovery and resource efficiency
• Support for compliance with WEEE and sustainability standards